Basic Operations#
In this section, we introduce the basic operations of a cfr.ClimateField.
Required data to complete this tutorial:
GISTEMP surface temperature: gistemp1200_GHCNv4_ERSSTv5.nc
Due to the new data fetching feature, the above datasets are not required to be downloaded manually.
[1]:
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
import cfr
print(cfr.__version__)
import numpy as np
2024.12.4
Load the test netCDF file as a ClimateField#
[13]:
fd = cfr.ClimateField().fetch(
'gistemp1200_GHCNv4_ERSSTv5', # URL points to the netCDF file OR a supported dataset name
vn='tempanomaly', # specify the name of the variable to load
)
fd.da # check the loaded `xarray.DataArray`
>>> The target file seems existed at: ./data/gistemp1200_GHCNv4_ERSSTv5.nc.gz . Loading from it instead of downloading ...
[13]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tempanomaly' (time: 1720, lat: 90, lon: 180)> Size: 111MB
array([[[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
...,
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan]],
[[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
...
[ 4.14 , 4.14 , 4.14 , ..., 4.14 ,
4.14 , 4.14 ],
[ 4.14 , 4.14 , 4.14 , ..., 4.14 ,
4.14 , 4.14 ],
[ 4.14 , 4.14 , 4.14 , ..., 4.14 ,
4.14 , 4.14 ]],
[[ 1.5699999, 1.5699999, 1.5699999, ..., 1.5699999,
1.5699999, 1.5699999],
[ 1.5699999, 1.5699999, 1.5699999, ..., 1.5699999,
1.5699999, 1.5699999],
[ 1.5699999, 1.5699999, 1.5699999, ..., 1.5699999,
1.5699999, 1.5699999],
...,
[ 3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , 3. ],
[ 3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , 3. ],
[ 3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , 3. ]]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 360B -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* time (time) object 14kB 1880-01-15 00:00:00 ... 2023-04-15 00:00:00
* lon (lon) float32 720B 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[14]:
fd = cfr.ClimateField().load_nc(
'./data/gistemp1200_GHCNv4_ERSSTv5.nc.gz', # path to the netCDF file; compressed data (.nc.gz) is also supported
vn='tempanomaly', # specify the name of the variable to load
)
fd.da # check the loaded `xarray.DataArray`
[14]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tempanomaly' (time: 1720, lat: 90, lon: 180)> Size: 111MB
array([[[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
...,
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan]],
[[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
...
[ 4.14 , 4.14 , 4.14 , ..., 4.14 ,
4.14 , 4.14 ],
[ 4.14 , 4.14 , 4.14 , ..., 4.14 ,
4.14 , 4.14 ],
[ 4.14 , 4.14 , 4.14 , ..., 4.14 ,
4.14 , 4.14 ]],
[[ 1.5699999, 1.5699999, 1.5699999, ..., 1.5699999,
1.5699999, 1.5699999],
[ 1.5699999, 1.5699999, 1.5699999, ..., 1.5699999,
1.5699999, 1.5699999],
[ 1.5699999, 1.5699999, 1.5699999, ..., 1.5699999,
1.5699999, 1.5699999],
...,
[ 3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , 3. ],
[ 3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , 3. ],
[ 3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , 3. ]]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 360B -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* time (time) object 14kB 1880-01-15 00:00:00 ... 2023-04-15 00:00:00
* lon (lon) float32 720B 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: meanTime slicing#
We may slice a ClimateField as like with xarray.DataArray:
[43]:
# get the 1st time point
fd[0].da
[43]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[16200 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
time object 1880-01-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[44]:
# get the first 5 time points
fd[:5].da
[44]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 5, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[81000 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1880-01-15 00:00:00 ... 1880-05-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[55]:
# get discrete data points
fd[[1, 5]].da
<class 'list'>
[55]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 2, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[32400 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1880-02-15 00:00:00 1880-06-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[53]:
# get all the months in a year
fd['1990'].da
<class 'str'>
[53]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 12, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[194400 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1990-01-15 00:00:00 ... 1990-12-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[65]:
# get all the months in a list of years
fd[['1990', '1995']].da
[65]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 24, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
array([[[ 0.35 , 0.35 , 0.35 , ..., 0.35 ,
0.35 , 0.35 ],
[ 0.35 , 0.35 , 0.35 , ..., 0.35 ,
0.35 , 0.35 ],
[ 0.35 , 0.35 , 0.35 , ..., 0.35 ,
0.35 , 0.35 ],
...,
[ 3.56 , 3.56 , 3.56 , ..., 3.56 ,
3.56 , 3.56 ],
[ 3.56 , 3.56 , 3.56 , ..., 3.56 ,
3.56 , 3.56 ],
[ 3.56 , 3.56 , 3.56 , ..., 3.56 ,
3.56 , 3.56 ]],
[[-0.69 , -0.69 , -0.69 , ..., -0.69 ,
-0.69 , -0.69 ],
[-0.69 , -0.69 , -0.69 , ..., -0.69 ,
-0.69 , -0.69 ],
[-0.69 , -0.69 , -0.69 , ..., -0.69 ,
-0.69 , -0.69 ],
...
[ 0.5 , 0.5 , 0.5 , ..., 0.5 ,
0.5 , 0.5 ],
[ 0.5 , 0.5 , 0.5 , ..., 0.5 ,
0.5 , 0.5 ],
[ 0.5 , 0.5 , 0.5 , ..., 0.5 ,
0.5 , 0.5 ]],
[[ 0.97999996, 0.97999996, 0.97999996, ..., 0.97999996,
0.97999996, 0.97999996],
[ 0.97999996, 0.97999996, 0.97999996, ..., 0.97999996,
0.97999996, 0.97999996],
[ 0.97999996, 0.97999996, 0.97999996, ..., 0.97999996,
0.97999996, 0.97999996],
...,
[-2.98 , -2.98 , -2.98 , ..., -2.98 ,
-2.98 , -2.98 ],
[-2.98 , -2.98 , -2.98 , ..., -2.98 ,
-2.98 , -2.98 ],
[-2.98 , -2.98 , -2.98 , ..., -2.98 ,
-2.98 , -2.98 ]]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1990-01-15 00:00:00 ... 1995-12-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[68]:
# get a time period
fd['1990':'2000'].da
[68]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 120, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[1944000 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1990-01-15 00:00:00 ... 1999-12-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[67]:
# get a time period with steps
fd['1990':'2000':5].da
[67]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 24, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[388800 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1990-01-15 00:00:00 ... 1999-08-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean[72]:
# get a time period with steps
fd['1990':'2001':5*12].da
[72]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 3, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[48600 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1990-01-15 00:00:00 ... 2000-01-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: meanRename the variable#
By renaming the variable, we are able to load some presets for visualization.
[29]:
fd = fd.rename('tas')
fd.da
[29]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 1720, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
[27864000 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1880-01-15 00:00:00 ... 2023-04-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: meanPlot a field map at a time point#
[30]:
fig, ax = fd['1990-11'].plot()
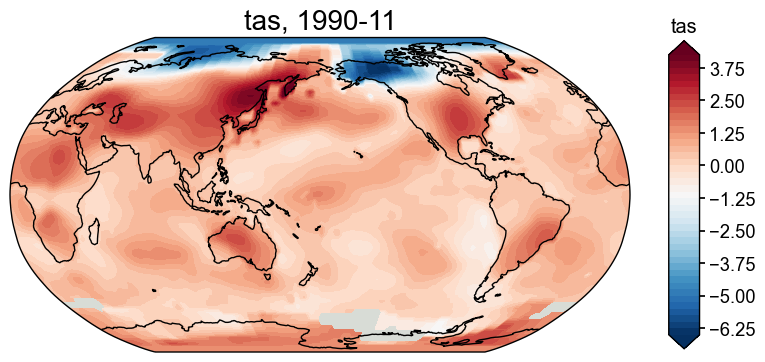
The default colorbar is not zero-centered. We may adjust as below:
[31]:
fig, ax = fd['1990-11'].plot(
levels=np.linspace(-5, 5, 21), # set levels for the colors
cbar_labels=np.linspace(-5, 5, 11), # set the labels for the bar
)
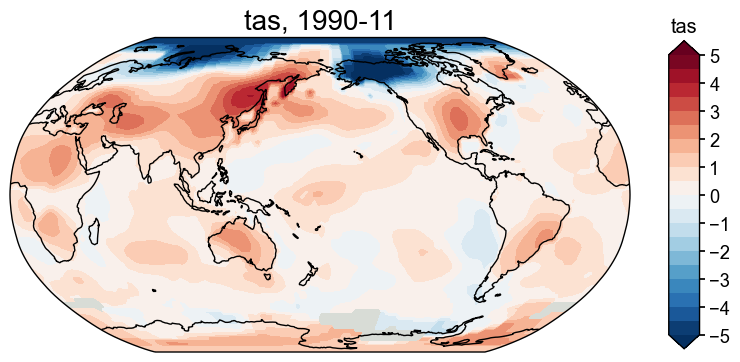
Get the anomaly field#
We may call the .get_anom() method, specifying a reference period, to calculate the anomaly field:
[32]:
fd_anom = fd.get_anom(ref_period=(1951, 2000))
fig, ax = fd_anom['1990-11'].plot(
levels=np.linspace(-5, 5, 21), # set levels for the colors
cbar_labels=np.linspace(-5, 5, 11), # set the labels for the bar
extend='both', # extend the bar
)
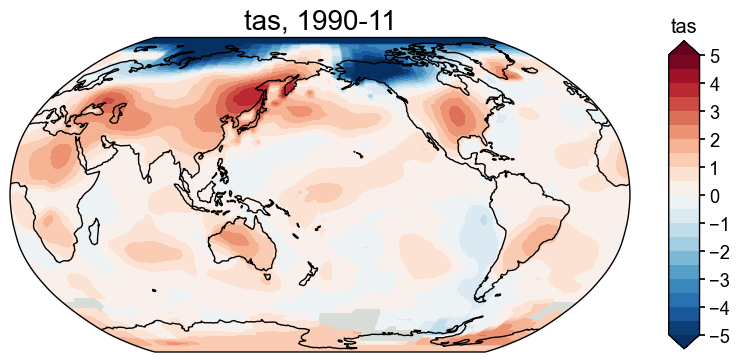
Center the field#
Similar to calculating the anomaly, sometimes we just want to center the values of a field against a reference period. With a cfr.ClimateField, we may call the .center() method to achieve that, again speciying a reference period:
[33]:
fd_center = fd.center(ref_period=(1951, 2000))
fig, ax = fd_center['1990-11'].plot(
levels=np.linspace(-5, 5, 21), # set levels for the colors
cbar_labels=np.linspace(-5, 5, 11), # set the labels for the bar
extend='both', # extend the bar
)
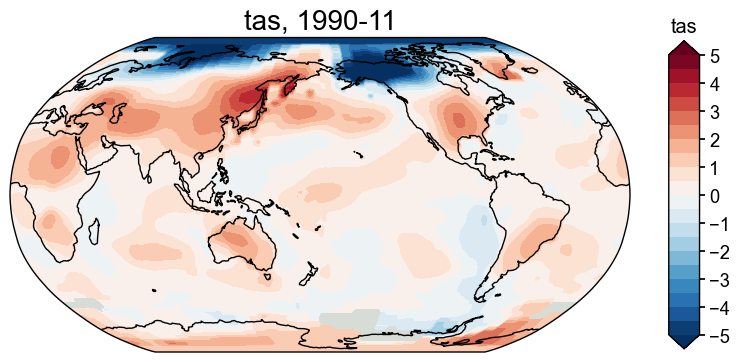
Annualize/Seasonalize a ClimateField#
It is common that we need to annualize/seasonalize a monthly data. With a ClimateField, we may call the .annualize() method with months as the argument to achieve the goal.
For instance, if we’d like to calculate the DJF annual data, simply:
[34]:
fd_djf = fd.annualize(months=[12, 1, 2])
fd_djf.da.time.values
[34]:
array([1880, 1881, 1882, 1883, 1884, 1885, 1886, 1887, 1888, 1889, 1890,
1891, 1892, 1893, 1894, 1895, 1896, 1897, 1898, 1899, 1900, 1901,
1902, 1903, 1904, 1905, 1906, 1907, 1908, 1909, 1910, 1911, 1912,
1913, 1914, 1915, 1916, 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923,
1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928, 1929, 1930, 1931, 1932, 1933, 1934,
1935, 1936, 1937, 1938, 1939, 1940, 1941, 1942, 1943, 1944, 1945,
1946, 1947, 1948, 1949, 1950, 1951, 1952, 1953, 1954, 1955, 1956,
1957, 1958, 1959, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1967,
1968, 1969, 1970, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1974, 1975, 1976, 1977, 1978,
1979, 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986, 1987, 1988, 1989,
1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000,
2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011,
2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022,
2023])
[35]:
fd_djf['1881'].da
[35]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 1, lat: 90, lon: 180)>
array([[[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
...,
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) int64 1881
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean
annualized: 1[36]:
fd_djf[-1].da
[36]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (lat: 90, lon: 180)>
array([[-1.8566667, -1.8566667, -1.8566667, ..., -1.8566667, -1.8566667,
-1.8566667],
[-1.8566667, -1.8566667, -1.8566667, ..., -1.8566667, -1.8566667,
-1.8566667],
[-1.8566667, -1.8566667, -1.8566667, ..., -1.8566667, -1.8566667,
-1.8566667],
...,
[ 5.4666667, 5.4666667, 5.4666667, ..., 5.4666667, 5.4666667,
5.4666667],
[ 5.4666667, 5.4666667, 5.4666667, ..., 5.4666667, 5.4666667,
5.4666667],
[ 5.4666667, 5.4666667, 5.4666667, ..., 5.4666667, 5.4666667,
5.4666667]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -89.0 -87.0 -85.0 -83.0 -81.0 ... 83.0 85.0 87.0 89.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
time int64 2023
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: mean
annualized: 1Regrid a ClimateField#
Regridding is also a common task. With a ClimateField, we may easily modify the spatial resolution of a field.
[37]:
fd_regrid = fd.regrid(np.linspace(-90, 90, 41), np.linspace(0, 360, 81))
fd_regrid.da
[37]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 1720, lat: 41, lon: 81)>
array([[[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
...,
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan]],
[[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
...
[ nan, 1.33999991, 1.24000001, ..., 1.30999994,
1.33999991, nan],
[ nan, 4.13999987, 4.13999987, ..., 4.13999987,
4.13999987, nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan]],
[[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan],
[ nan, 1.56999993, 1.56999993, ..., 1.56999993,
1.56999993, nan],
[ nan, 3.11999989, 2.74000001, ..., 4.02999973,
3.75 , nan],
...,
[ nan, 4.80999994, 4.82999992, ..., 4.46999979,
4.5999999 , nan],
[ nan, 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , nan],
[ nan, nan, nan, ..., nan,
nan, nan]]])
Coordinates:
* time (time) object 1880-01-15 00:00:00 ... 2023-04-15 00:00:00
* lat (lat) float64 -90.0 -85.5 -81.0 -76.5 -72.0 ... 76.5 81.0 85.5 90.0
* lon (lon) float64 0.0 4.5 9.0 13.5 18.0 ... 346.5 351.0 355.5 360.0
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: meanCrop a cfr.ClimateField#
With a cfr.ClimateField, we may crop a spatial domain by calling the .crop() method, specifying the arguments lat_min, lat_max, lon_min, lon_max:
[38]:
fd_crop = fd.crop(-35, 35, 0, 360)
fd_crop.da
[38]:
<xarray.DataArray 'tas' (time: 1720, lat: 36, lon: 180)>
[11145600 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* lat (lat) float32 -35.0 -33.0 -31.0 -29.0 -27.0 ... 29.0 31.0 33.0 35.0
* lon (lon) float32 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 ... 351.0 353.0 355.0 357.0 359.0
* time (time) object 1880-01-15 00:00:00 ... 2023-04-15 00:00:00
Attributes:
long_name: Surface temperature anomaly
units: K
cell_methods: time: meanCalculate the weighted mean of a sptial area#
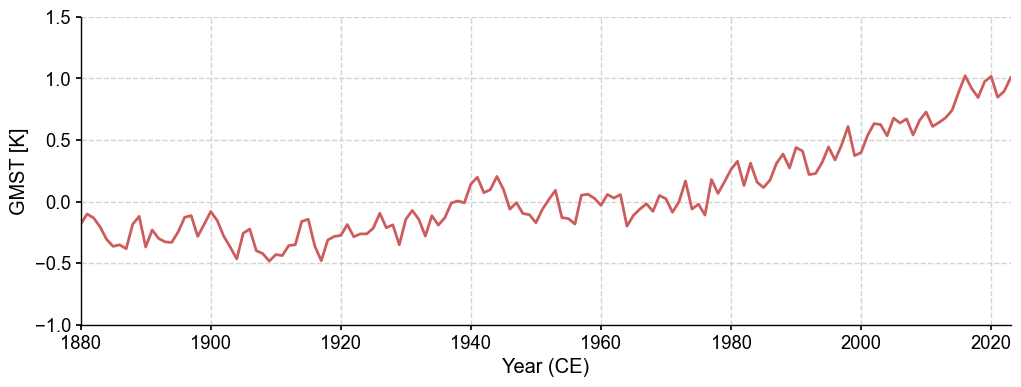
Lots of climatic indices require to calculate the weighted mean of a spatial area, e.g., the global mean surface temperature (GMST), NINO3.4, etc.
With a cfr.ClimateField, we may call the .geo_mean() method to calculate that quantity, again specifying the arguments lat_min, lat_max, lon_min, lon_max.
[39]:
gmst = fd.annualize().geo_mean() # by default, the area is global
fig, ax = gmst.plot(ylabel='GMST [K]', linewidth=2, ylim=(-1, 1.5))
[40]:
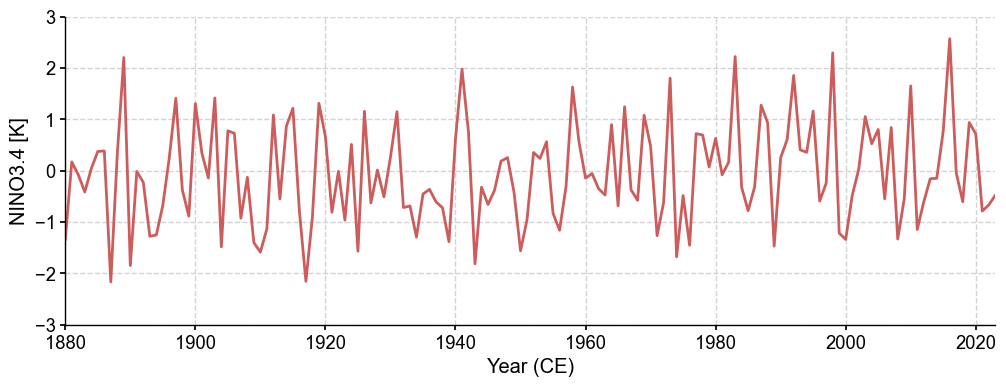
nino34 = fd.annualize(months=[12, 1, 2]).geo_mean(
lat_min=-5, lat_max=5,
lon_min=np.mod(-170, 360), lon_max=np.mod(-120, 360)
)
fig, ax = nino34.plot(ylabel='NINO3.4 [K]', linewidth=2, ylim=(-3, 3))
Validate a field against another#
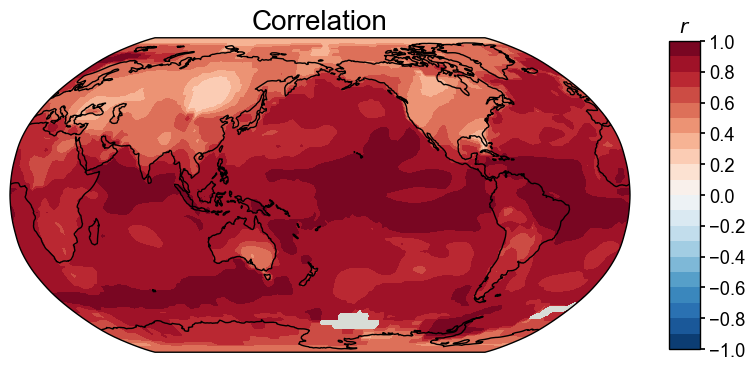
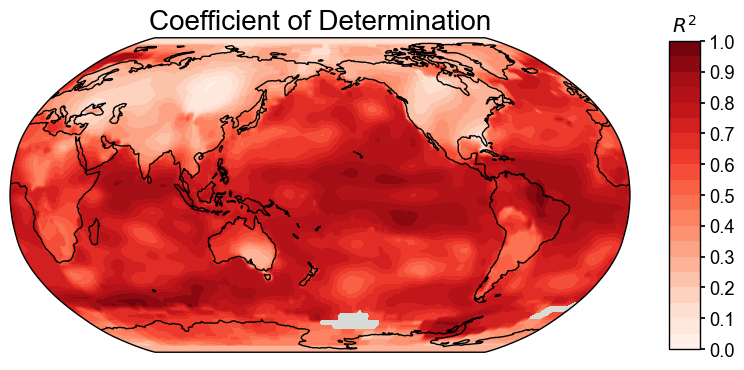
We may compare two cfr.ClimateFields by calling the .compare() method. Here as an example, we compare the calendar year annualized field with the JJA annualized field, with three different metrics:
[15]:
for stat in ['corr', 'R2', 'CE']:
valid_fd = fd['1880':'2000'].annualize().compare(
fd['1880':'2000'].annualize(months=[6, 7, 8]), stat=stat)
fig, ax = valid_fd.plot()
[ ]:
